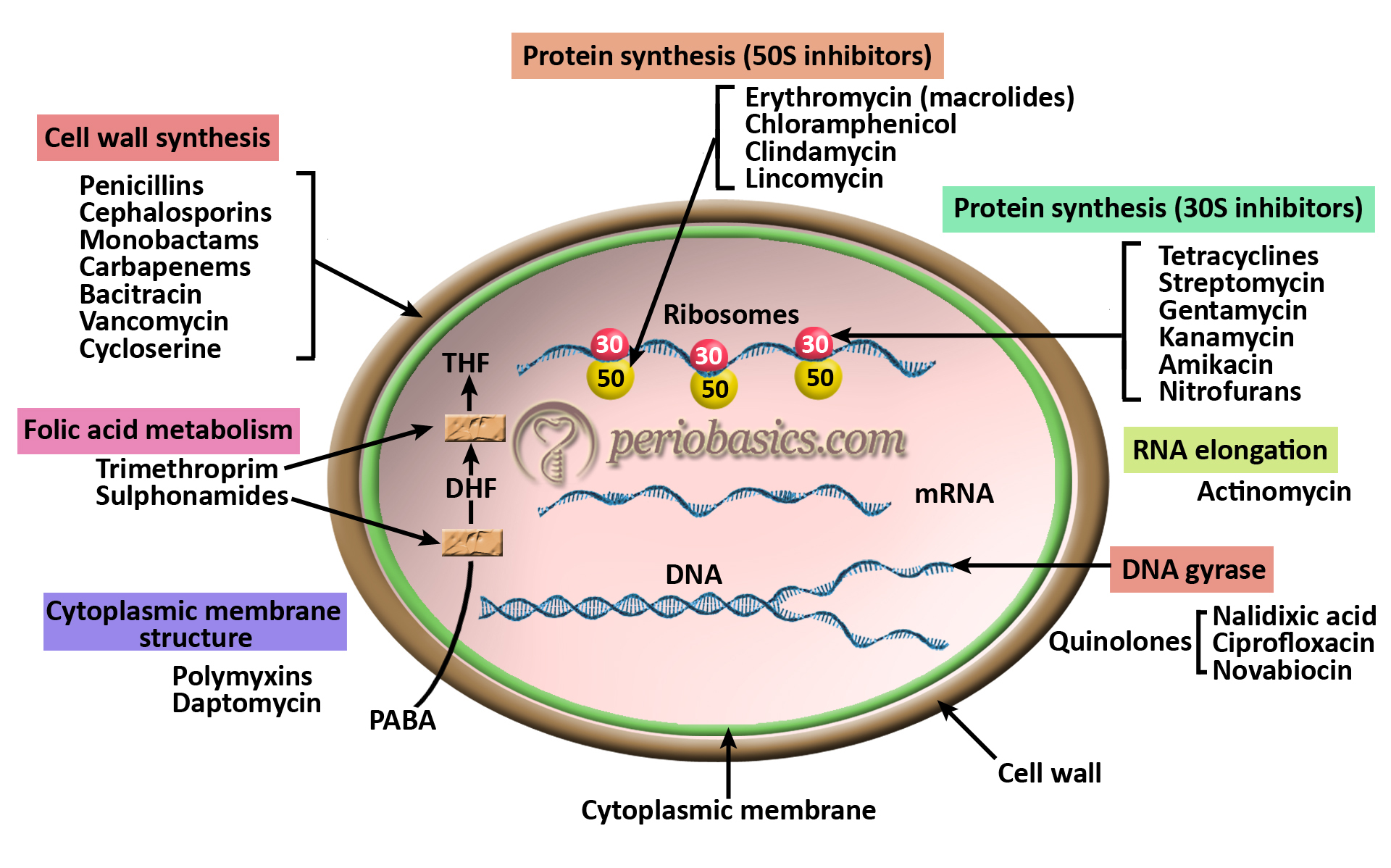
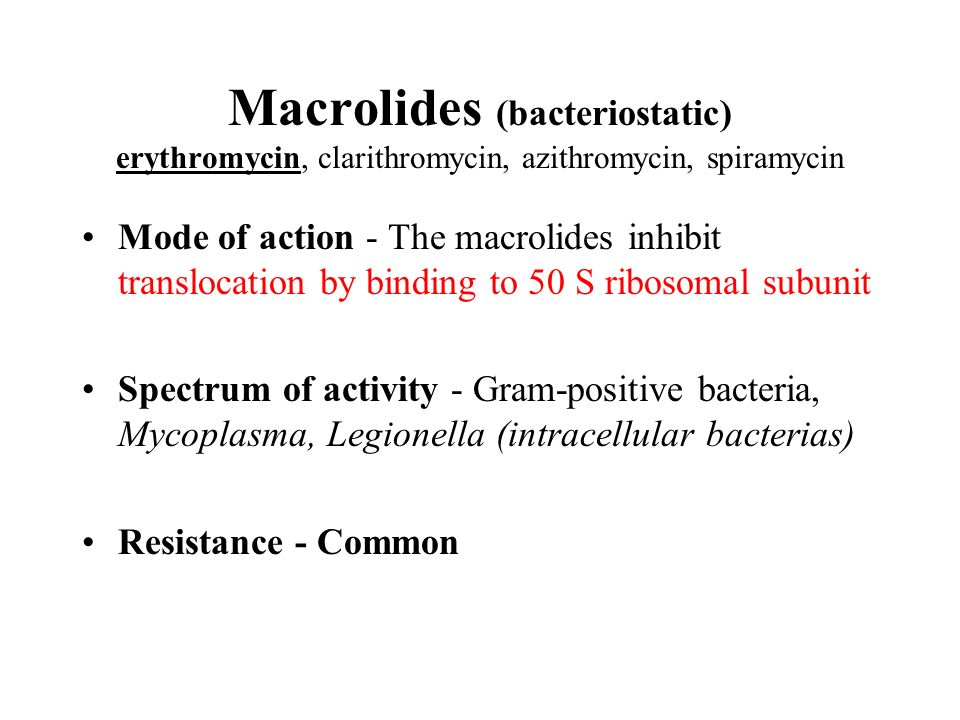
The similarity between these mechanisms and their relation to the general mode of macrolide action is discussed and the discrepancies between currently available data are highlighted Key words macrolides, erythromycin, ketolides, azithromycin, clarithromycin, tylosin, carbomycin, spiramycin, ribosome, resistance INTRODUCTION Antibiotics types based on mechanism of action Drugs and Pharmacology Inhibit cell wall synthesis beta lactams Natural penicillins Penicillin G Penicillin V Benzathine P Procaine P, Penicilllinase R diarrhoea and dyspepsia Erythromycin Clarithromycin Azithromycin Roxithromycin Spiramycin Tylosin TelithromycinErythromycin Antibiotic Class Macrolide Antimicrobial Activity Grampositive bacteria, mycoplasma pneumoniae, chlamydia trachomatis, chlamydia pneumoniae, chlamydia psittaci, ureaplasma urealyticum, legionella pneumophila, campylobacter jejuni, bordatella pertussis Mechanism of Action Macrolides are inhibitors of protein synthesis
Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Jmedchem 6b Rand 3dkrshtg
Mechanism of action of spiramycin and other macrolides
Mechanism of action of spiramycin and other macrolides-The possible immunomodulatory mechanism of action of spiramycin was studied by measuring the local IgA deposition in small intestinal mucosa by PAP technique 4 weeks pi The levels of IgA in small intestine were higher in SPtreated group as compared with theThe possible immunomodulatory mechanism of action of spiramycin was studied by measuring the local IgA deposition in small intestinal mucosa by PAP technique 4 weeks pi The levels of IgA in small intestine were higher in SPtreated group as compared with the nontreated group



Spiramycin Tablets Manufacturer Supplier India Buy Online
Spiramycin is a treatment that is included in the macrolide antibiotic class Spiramycin can be used to treat bacterial infections, one of the uses of spiramycin is to treat Toxoplasma gondii (toxoplasmosis) infection Spiramycin has a mechanism of action to inhibit bacterial growth Mechanism of action of Spiramycin & Metronidazole Rodogyl is a combination of the antibiotic spiramycin of the macrolide family and the antibiotic metronidazole of the nitro5imidazole family, specifically for infectious oral disease Contraindications Do not use Rodogyl in patients who are hypersensitive to any of the ingredients in the drug The mechanism of action of Spiramycin & Metronidazole Rodogyl is a combination of spiramycin antibiotic of the macrolide family and metronidazole antibiotic of the nitro5imidazole family, specifically for infectious oral diseases Contraindicated Do not use Rodogyl for patients with hypersensitivity to any components of the drug
They have one or more sugars which can be amino sugars, nonnitrogenousMechanism of Action of Spiramycin Spiramycin is a member of macrolide antibiotic It binds to the 50S sub unit of bacterial ribosome and inhibits translocationie they interfere with the transfer of the newly formed peptide chain from the A site to the P site and fails to expose the A site So that A site is unable to bind with the next aminoacyl t RNA complexRovamycin 15million Tablets About Spiramycin Macrolide Antibiotic, Antibacterial (systemic,antiprotozoal,In toxoplasmosis, cryptosporidiosis Mechanism of Action of Spiramycin Spiramycin is a member of macrolide antibiotic It binds to the 50S sub unit of bacterial ribosome and inhibits translocationie they interfere with the transfer of the newly formed peptide chain
The mechanism of action of macrolides has been a matter of controversy for some time Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 11 stoichiometry This antibiotic is a potent inhibitor of the binding to the ribosome of both donor and acceptor substratesThe macrolidelincosamidestreptogramin B class (MLS) of antibiotics contains structurally different but functionally similar drugs, that all bind to the 50S ribosomal subunit It has been suggested that these compounds block the path by which nascent peptides exit the ribosome We have studied the mechanisms of action of four macrolides (erythromycin, josamycin, spiramycin and Macrolides are generally bacteriostatic, although some of these drugs may be bactericidal at very high concentrations The mechanism of action of macrolides has been a matter of controversy for some time Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 1 1 stoichiometry
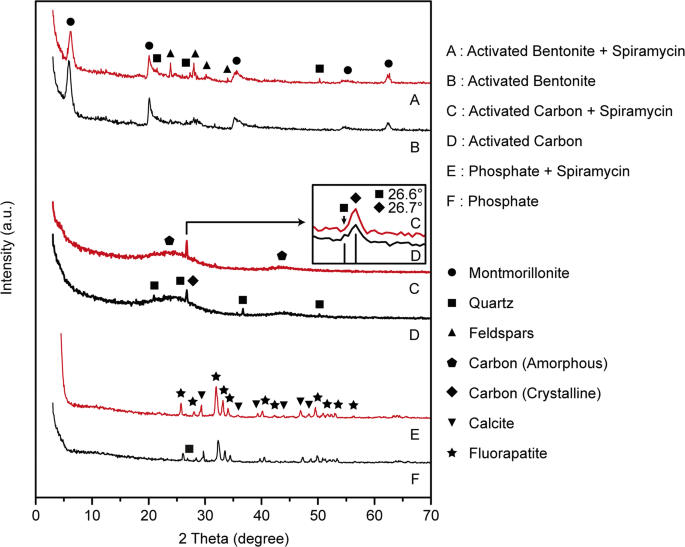



Spiramycin Adsorption Behavior On Activated Bentonite Activated Carbon And Natural Phosphate In Aqueous Solution Springerlink




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Clinical Microbiology And Infection
It has been suggested that these compounds block the path by which nascent peptides exit the ribosome We have studied the mechanisms of action of four macrolides (erythromycin, josamycin, spiramycin and telithromycin), one lincosamide (clindamycin) and one streptogramin B (pristinamycin IA)Spiramycin acts by decreasing transmission to the fetus and has been shown to decrease transmission rates by 60% 14 It concentrates in the placenta but does not cross and should be continued even when PCR testing on amniotic fluid is negative because of possible later fetal infection 1 If pregnant women are suspected of acquiring the infection late in the second trimester or during the third trimester, pyrimethamine, The mechanism of action of macrolides has been a matter of controversy for some time Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 11 stoichiometry This antibiotic is a potent inhibitor of the binding to the ribosome of both donor and acceptor substrates
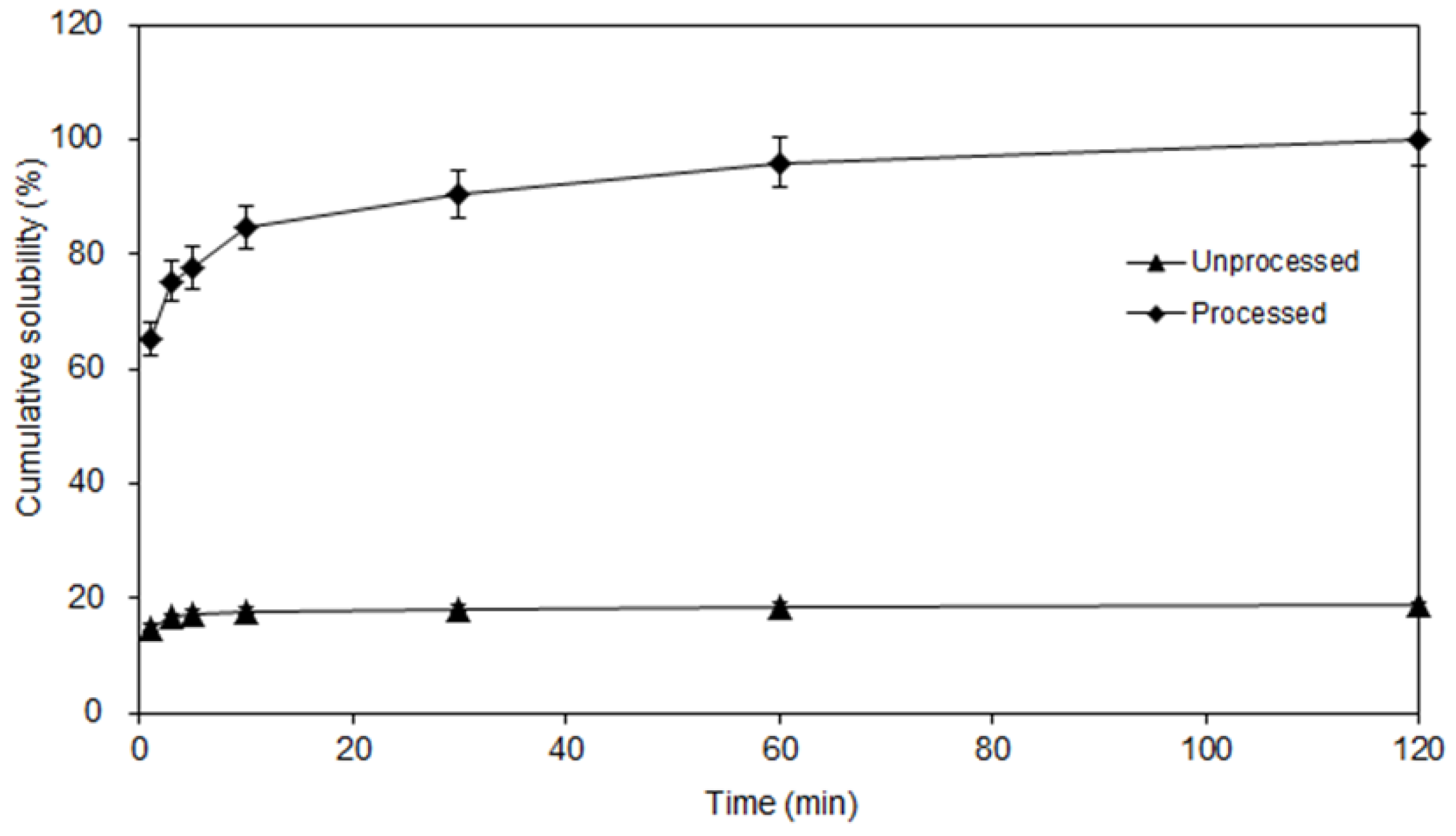



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Spiramycin Toku E
The similarity between these mechanisms and their relation to the general mode of macrolide action is discussed and the discrepancies between currently available data are highlighted Keywords macrolides, erythromycin, ketolides, azithromycin, clarithromycin, tylosin, carbomycin, spiramycin, ribosome, resistanceThe mechanism of action of macrolides has been a matter of controversy for some time Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 1 1 stoichiometry This antibiotic is a potent inhibitor of the binding to the ribosome of both donor and acceptor substrates Protein synthesis is catalysed by ribosomes and cytoplasmic factors Bacterial ribosomes (70S) are made up of 2 subunits (50S and 30S) containing ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and ribosomal proteins the 30S binds messenger RNA and begins the ribosomal cycle (initiation), whereas 50S binds transfer RNA (tRNA) derivatives and controls elongation The key reaction,




Pdf Spiramycin Renaissance
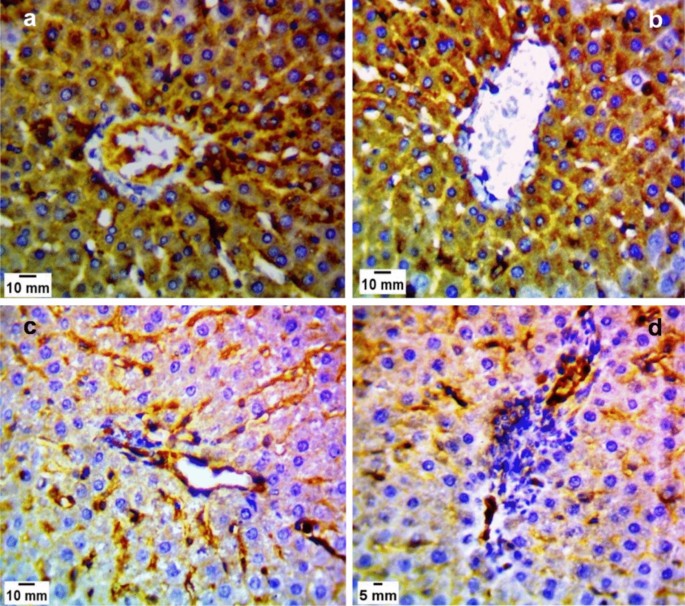



Effect Of Spiramycin Versus Aminoguanidine And Their Combined Use In Experimental Toxoplasmosis Springerlink
Rima Pharmacology 0 Spiramycin is a member of macrolide antibiotic Macrolide antibiotics are a group of antibiotics which are composed of a macrocyclic lactone of different ring sizes to which one or more deoxy sugars are attached The ring is either 14, 15 or 16 membered Spiramycin has 16 membered rings It was discovered in 1952The exact mechanism of action is unknown at this time but the 3' position contains an amide linkage instead of the normal ester linkage of tRNA That makes the molecule much more resistant to hydrolysis and stops the ribosome Puromycin is selective for either prokaryotes or eukaryotes Also of note, puromycin is critical in mRNA display1 Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jun;94(6) The mechanism of action of antibiotics, particularly spiramycin Article in French VIDEAU D
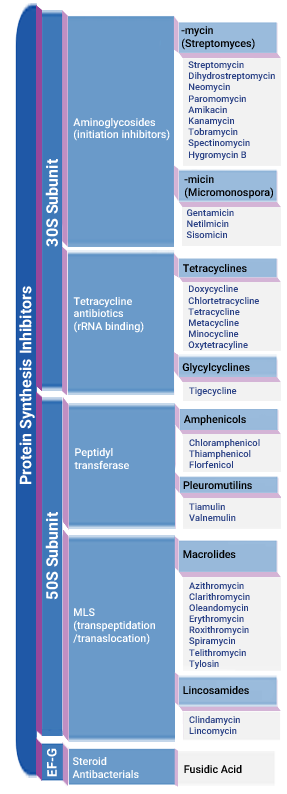



Antibiotic Classification Table



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals
I The experiments described in this paper were devised with the object of ascertaining something about the mechanism of action of certain drugs, eg, parafuchsin, trypaflavine and neosalvarsan, on trypanosomes, and especially whether their action was direct Rats were inoculated with a strain of nagana very sensitive to trypaflavine and salvarsan, and at the height of the infection wereAbstract The term macrolide has been applied to members of a group of structurally related antibiotics produced by species of streptomyces All macrolide antibiotics (W oodward, 1957) contain a large lactone ring (aglycone of 12 to 22 atoms) which contain few double bonds and no nitrogen atoms;Download Citation StructureActivity Relationships And Mechanism Of Action Of Macrolides Derived From Erythromycin As Antibacterial Agents Enormous efforts were focused on the 3




Spiramycin Antibiotic Activities Bacteria



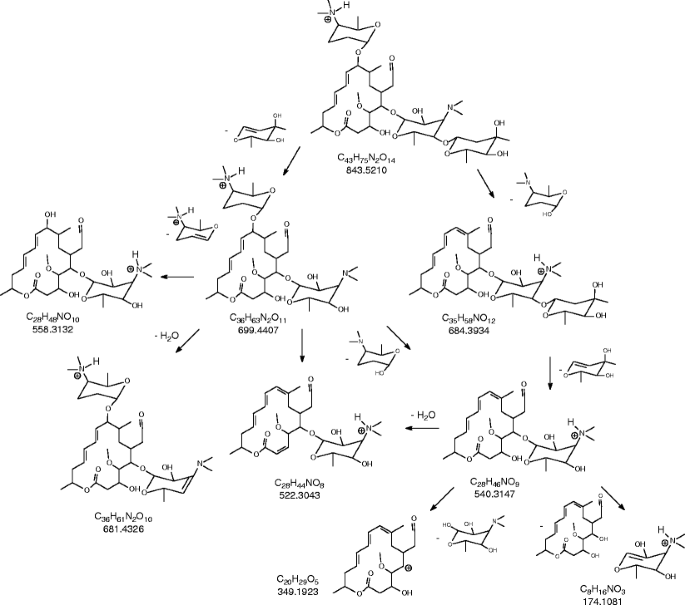
Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem
Both the Golgi network and recycling endosome play important roles in the packaging of proteins into vesicles that are destined for secretion, a process that is exploited by viruses to facilitate their replication and spread Altering the pH of these organelles may therefore interfere with these intracellular viral activitiesThe mechanism of action involves the inhibition of microbial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and interfering with peptide chain initiation (Tenson et al 03;Although the exact mechanism of action is unclear, artemisinins appear to act as prodrugs that are metabolized by target cells to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) When toxicity is a concern, spiramycin, a macrolide protein synthesis inhibitor, is typically administered for the treatment of



Spiramycin 3million Tablets Rosheta




Stylized Cells Depicting The Transport Metabolism And Mechanism Of Download Scientific Diagram
Spiramycin is a macrolide originally discovered as product of Streptomyces ambofaciens, with antibacterial and antiparasitic activities Although the specific mechanism of action has not been characterized, spiramycin likely inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosomeThe mechanism of action of macrolides has been a matter of controversy for some time Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 1 1 stoichiometry This antibiotic is a potent inhibitor of the binding to the ribosome of both donor and acceptor substrates Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic with an antibacterial spectrum similar to erythromycin and clindamycin It is bacteriostatic at serum concentrations but may be bactericidal at achievable tissue concentrations The mechanism of action is unclear, but it acts on the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes and interferes with translocation



Acetyl Spiramycin Tablet Beijingyaowuyanjiuyuan
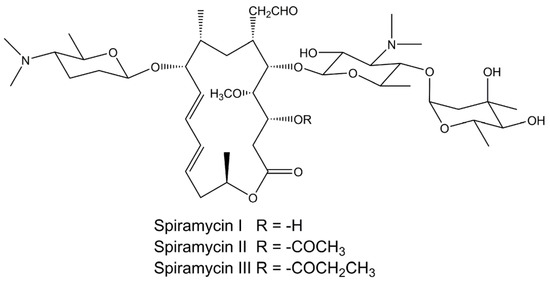



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html
Mechanism of action Daptomycin is a cyclic lipopeptide natural product that is active against Grampositive bacteria only The mechanism of action involves binding (in the presence of calcium ions) to bacterial membranes of both growing and stationary phase cells causing depolarisation and leading to a rapid inhibition of protein, DNA, and RNA synthesis AZITHROMYCIN iv ROXITHROMYCIN v SPIRAMYCIN KETOLIDES i TELITHROMYCIN 5 MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits protein synthesis by reversibly binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit Suppression of RNA dependent protein synthesis by inhibition of translocation of mRNA Typically bacteriostatic activity Bactericidal at high concentrations against veryThe similarity between these mechanisms and their relation to the general mode of macrolide action is discussed and the discrepancies between currently available data are highlighted Keywords macrolides , erythromycin , ketolides , azithromycin , clarithromycin , tylosin , carbomycin , spiramycin , ribosome , resistance




Clindamycin Wikipedia




Spiramycin Semantic Scholar
Mechanism of action and spectrum of activity7 43 Pharmacokinetics first macrolide intended for animal use was spiramycin, which was introduced in the early 1960ies, followed by erythromycin and tylosin (Prescott 08) A chemically modified tylosin, tylvalosinMacrolides have been used in the treatment of infectious diseases since the late 1950s Since that time, a finding of antagonistic action between erythromycin and spiramycin in clinical isolates1 led to evidence of the biochemical mechanism and to the current understanding of inducible or constitutive resistance to macrolides mediated by erm genes containing, respectively, the Article Views are the COUNTERcompliant sum of full text article downloads since November 08 (both PDF and HTML) across all institutions and individuals




Spiramycin Semantic Scholar




Congenital Toxoplasmosis What Is The Evidence For Chemoprophylaxis To Prevent Fetal Infection Mandelbrot Prenatal Diagnosis Wiley Online Library
The mechanism of action of pholcodine is directly performed in the medulla oblongata In this site, it exerts analgesic properties on the peripheric reflexogenic receptors This site is commonly known as the "cough center" DrugBank 9 Use and Manufacturing Mechanism of action In order to replicate, bacteria require a specific process of protein synthesis, enabled by ribosomal proteins 9 Erythromycin acts by inhibition of protein synthesis by binding to the 23S ribosomal RNA molecule in the 50S subunit of ribosomes in susceptible bacterial organismsThe antibiotic action involves inhibition of protein synthesis in the bacterial cell during translocation Resistance to spiramycin can develop by several mechanisms and its prevalence is to a considerable extent proportional to the frequency of prescription in a given area



2



Spiramycin Tablets Manufacturer Supplier Exporter From India
The combination of alcohol and metronidazole has been said to cause disulfiram type reactions in about 10% of individuals with sudden onset of excitement, giddiness, flushing, nausea, headache, hypotension and dyspnoea However the mechanism ofMechanism of Action of Spiramycin Spiramycin is a member of macrolide antibiotic It binds to the 50S sub unit of bacterial ribosome and inhibits translocationie they interfere with the transfer of the newly formed peptide chain from the A site to the P site and fails to expose the A site So that A site is unable to bind with the next aminoacyl t RNA complex



Spiramycin 1 5million Tablets Rosheta



Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Jmedchem 6b Rand 3dkrshtg



Fate Of Antibacterial Spiramycin In River Waters Springerlink



Chemotherapeutic Agents Used In Periodontics Periobasics Com



Q Tbn And9gcskpbplqnejpoqrywrytlz1pj8 403csl Jggjyfs8ooau0s5yw Usqp Cau
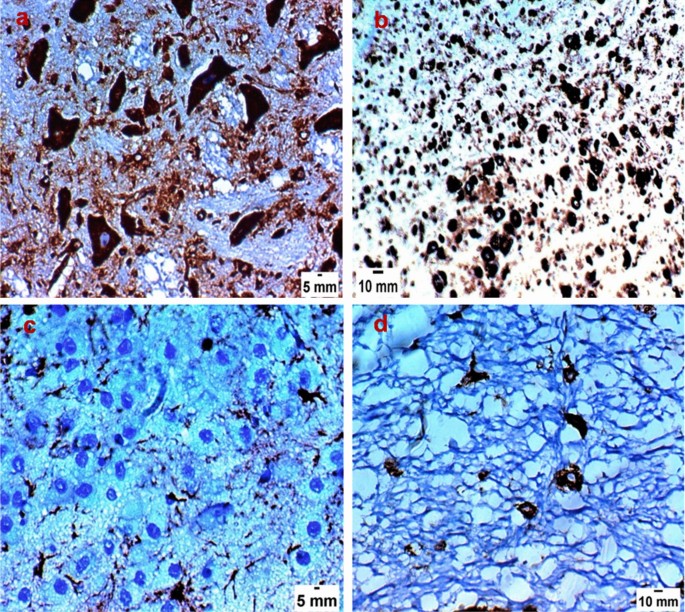



Effect Of Spiramycin Versus Aminoguanidine And Their Combined Use In Experimental Toxoplasmosis Springerlink



Rovamycin 3million Tablets Rosheta
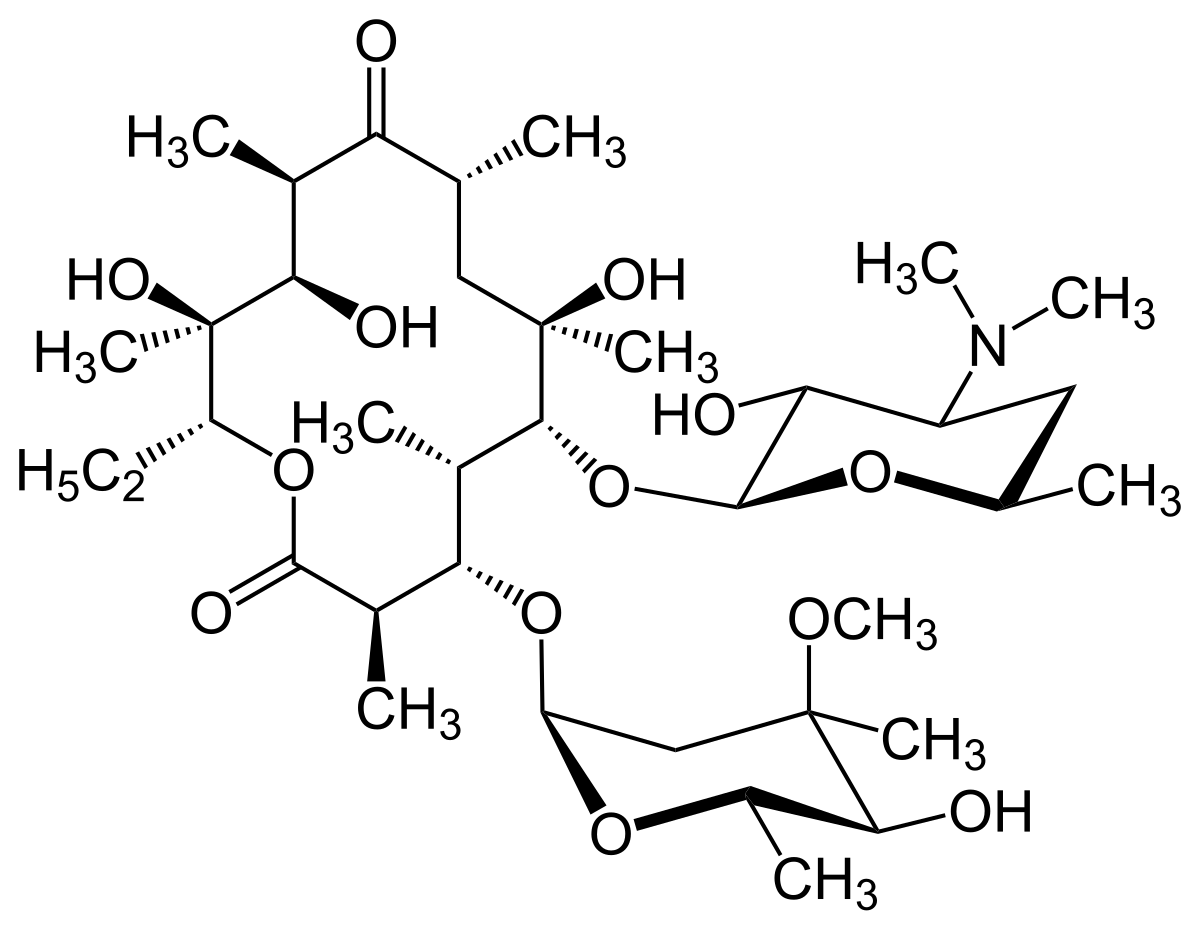



Macrolide Wikipedia



Www Chemie Tu Darmstadt De Media Ak Fessner Damocles Pdf 16 Spiramycin Pdf
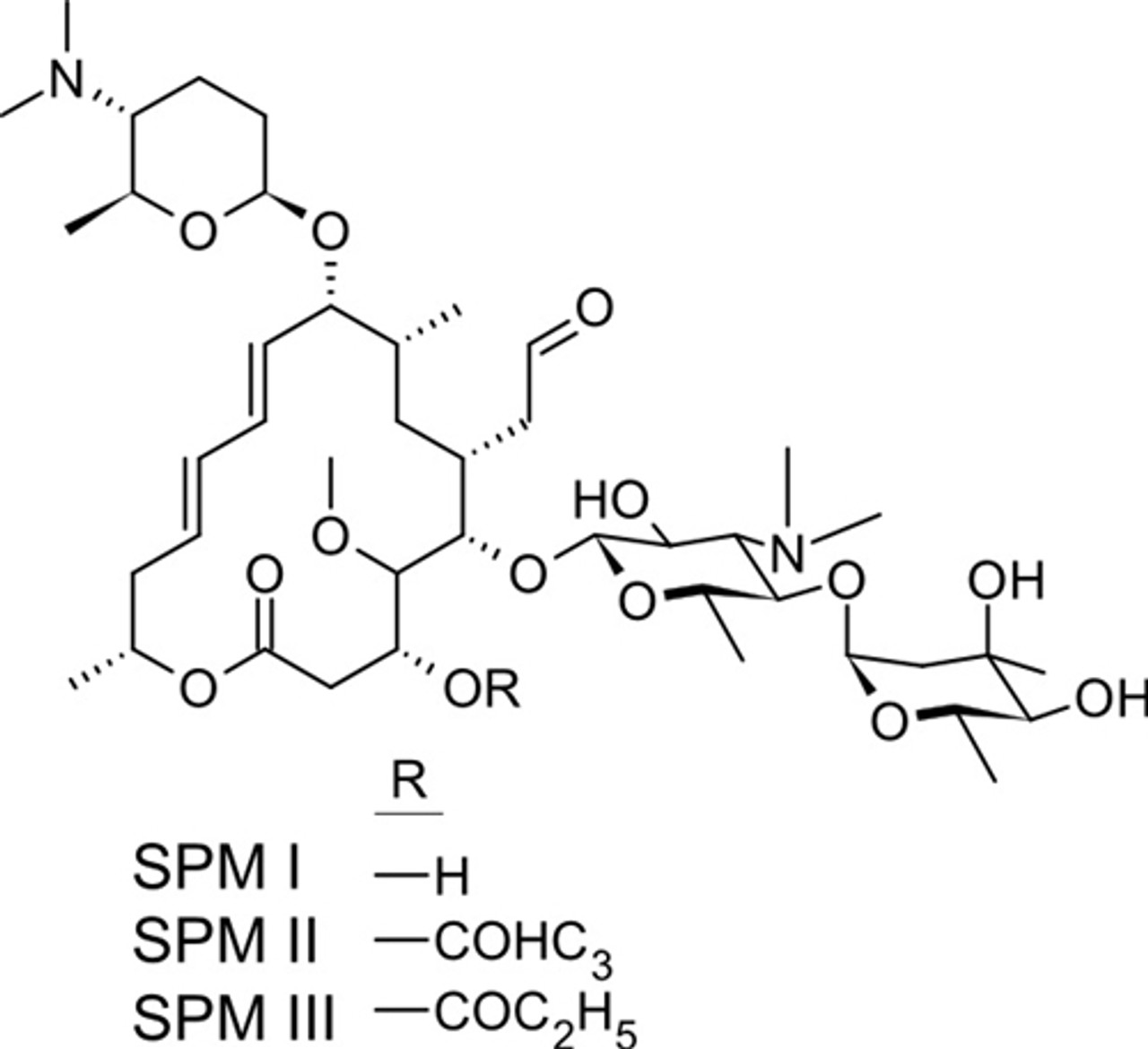



Spiramycin Toku E




Spiramycin Tablets Manufacturer Supplier India Buy Online



1
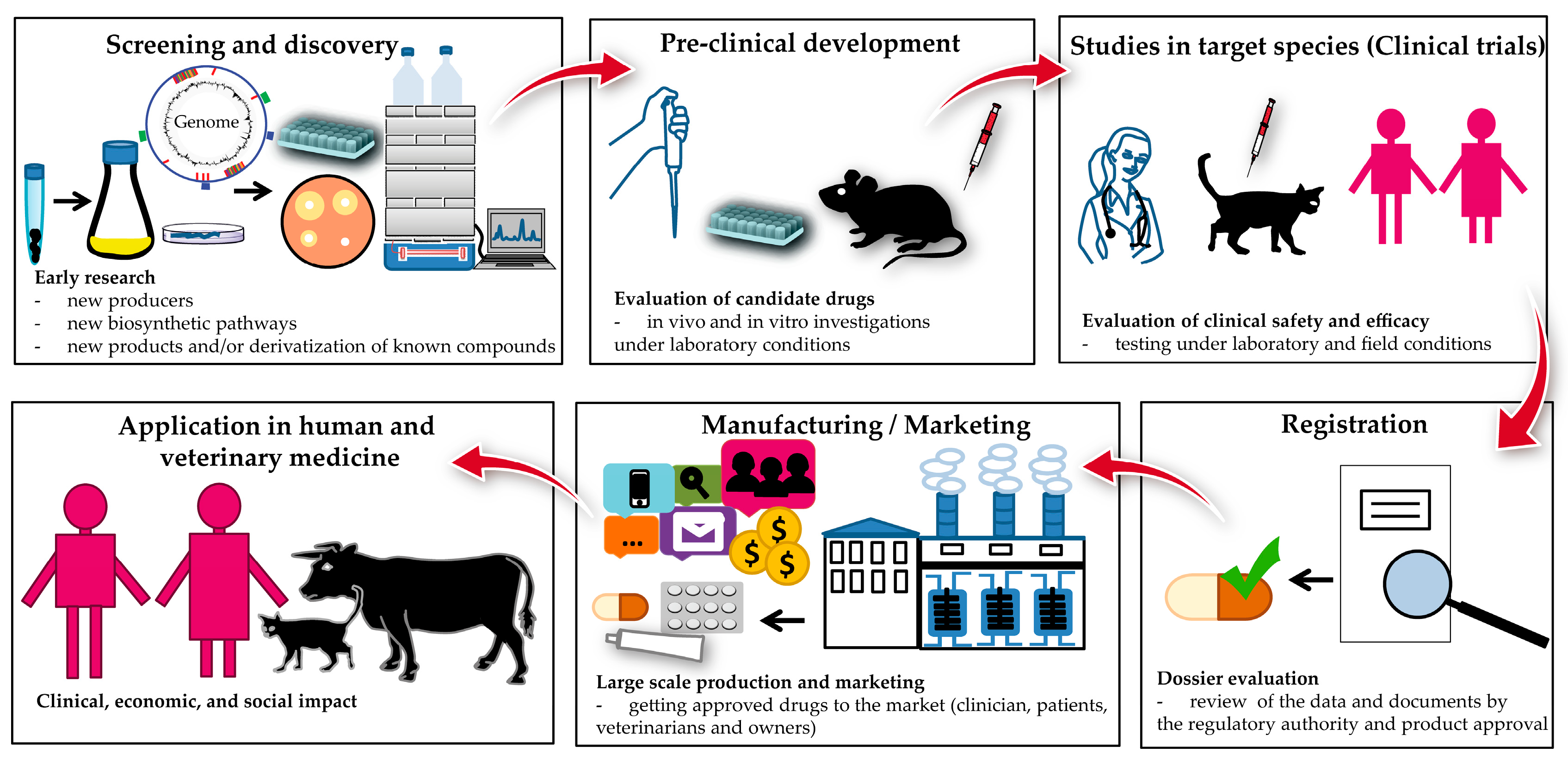



Antibiotics Free Full Text Actinomycete Derived Polyketides As A Source Of Antibiotics And Lead Structures For The Development Of New Antimicrobial Drugs Html




Spiramycin 8025 81 8 Tci Europe N V



Pharmacology Of Spiromycin Biopharma Notes




Drugs Compounds With Known Mechanisms Of Action On Life Stages Of T Download Scientific Diagram




Spiramycin From Streptomyces Sp Vetranal Analytical Standard Mixture Of Isomers 8025 81 8




Effect Of Ph On Spiramycin A And Metronidazole B Adsorption On Raw Download Scientific Diagram
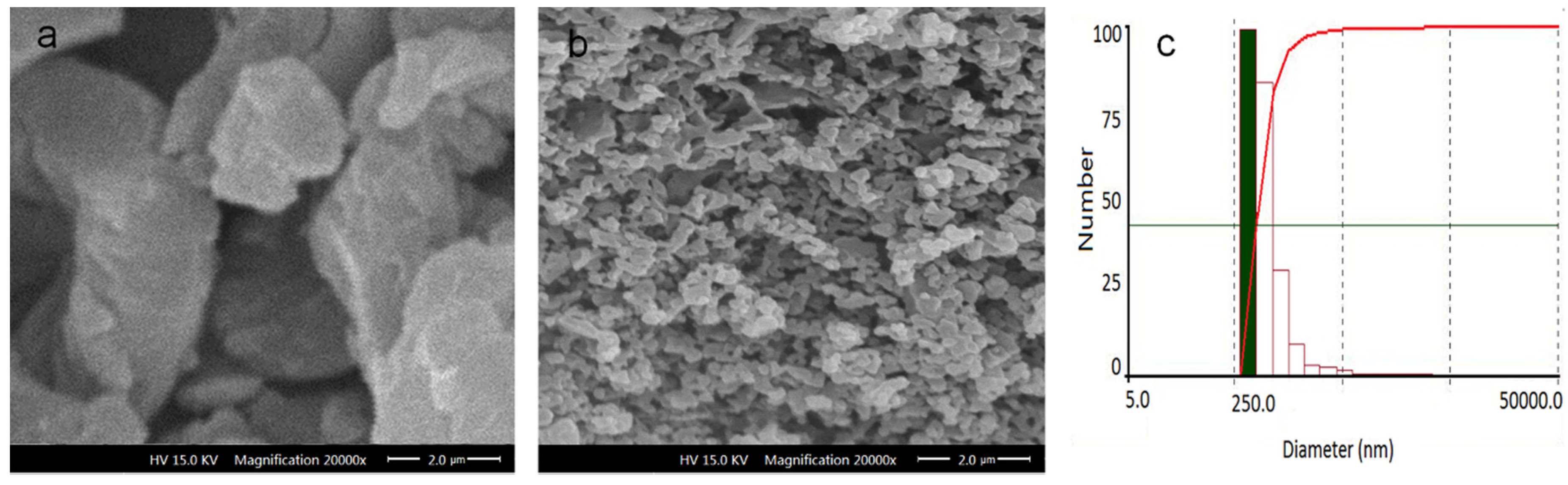



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Remarkable Histopathological Improvement Of Experimental Toxoplasmosis Treated With Spiramycin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Research Square
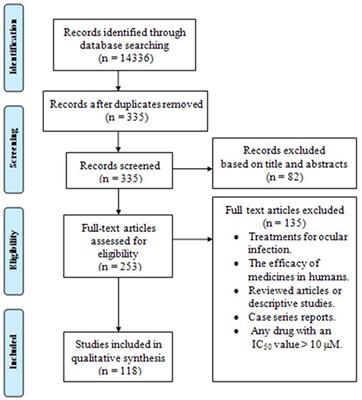



Frontiers A Systematic Review Of In Vitro And In Vivo Activities Of Anti Toxoplasma Drugs And Compounds 06 16 Microbiology



Rovamycin 1 5million Tablets Rosheta




Spiramycin Tablets At Rs 1375 Box Gidc Vatwa Ahmedabad Id



Academic Oup Com Jac Article Pdf 22 Supplement B 13 22 Supplement B 13 Pdf




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




Spiramycin Tablets Supplier Manufacturer Exporter India
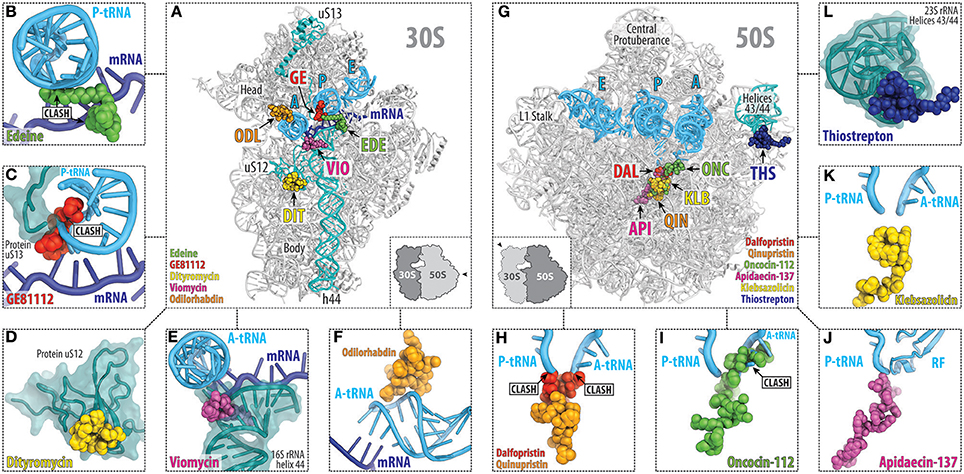



Frontiers The Mechanisms Of Action Of Ribosome Targeting Peptide Antibiotics Molecular Biosciences




Medical University Of Sofia Faculty Of Me Department



Pharmacokinetics Of Spiramycin In The Rhesus Monkey Transplacental Passage And Distribution In Tissue In The Fetus Abstract Europe Pmc



Www Chemie Tu Darmstadt De Media Ak Fessner Damocles Pdf 16 Spiramycin Pdf




Macrolide Antibiotics Spiramycin Carbomycin Angolamycin Methymycin And Lancamycin Springerlink




Remarkable Histopathological Improvement Of Experimental Toxoplasmosis Treated With Spiramycin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Research Square



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Figure 1 From The Mechanism Of Action Of Macrolides Lincosamides And Streptogramin B Reveals The Nascent Peptide Exit Path In The Ribosome Semantic Scholar




Spiramycin Tablets



Www Chemie Tu Darmstadt De Media Ak Fessner Damocles Pdf 16 Spiramycin Pdf




Kitasamycin An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Dspace Nwu Ac Za Bitstream Handle Van Eeden R Chapter 3 Pdf Sequence 4 Isallowed Y




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




Minimum Influent Concentrations Of Oxytetracycline Streptomycin And Spiramycin In Selecting Antibiotic Resistance In Biofilm Type Wastewater Treatment Systems Sciencedirect
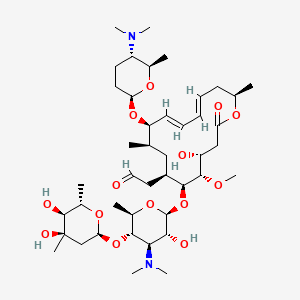



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem




Successful Treatment Of Acute Experimental Toxoplasmosis By Spiramycin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Sciencedirect




Is Spiramycine A Macrolide Ballya
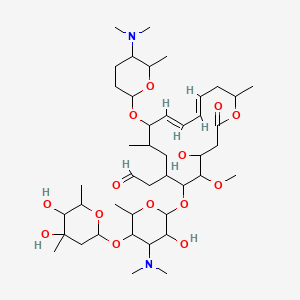



Spiramycin スピラマイシン New Drug Approvals



Q Tbn And9gcr9ohc8k8xdklq3 Vpmbg8 G8izttazf3lfsyvoxor 7xtdmk Usqp Cau
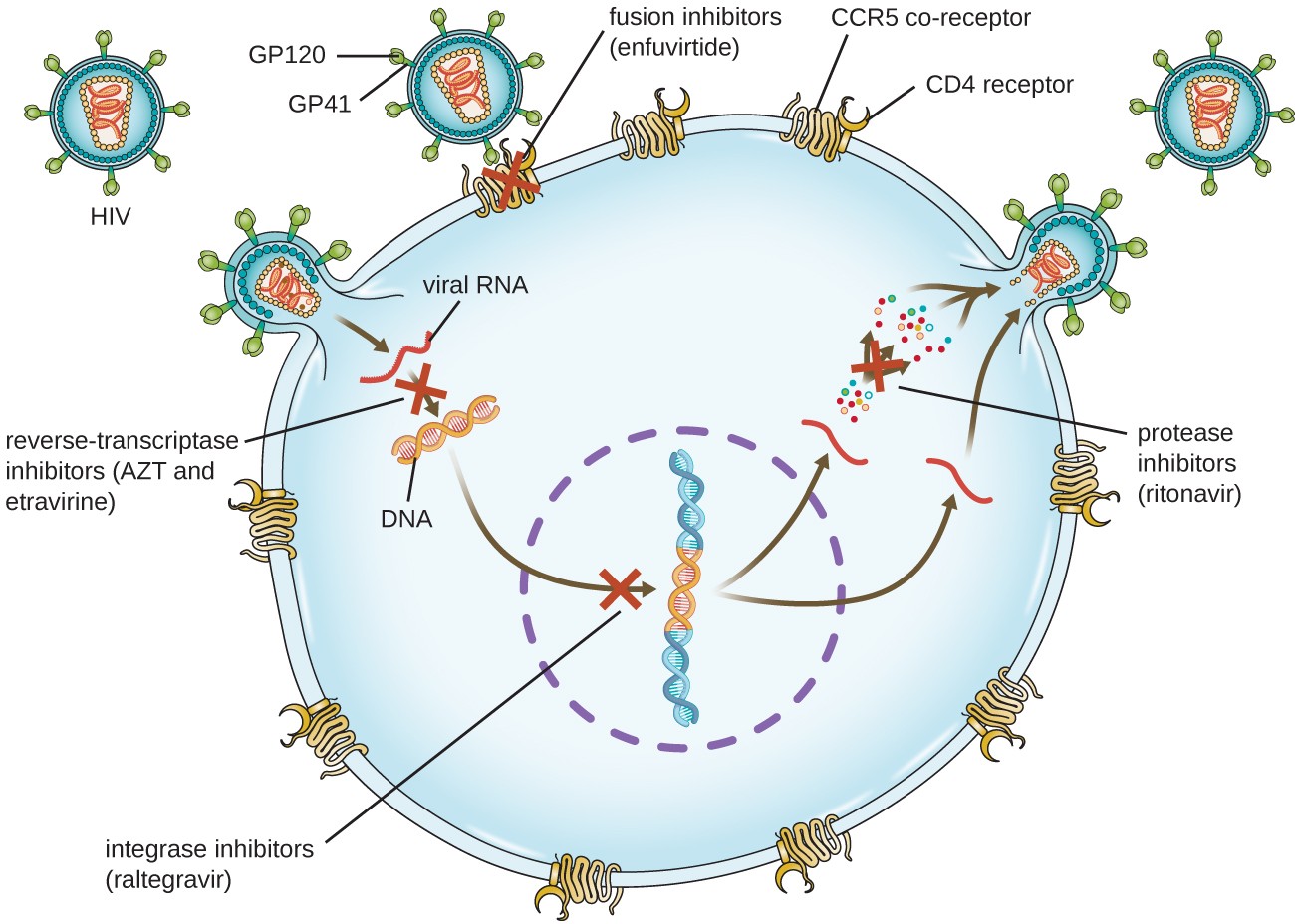



Mechanisms Of Other Antimicrobial Drugs Microbiology
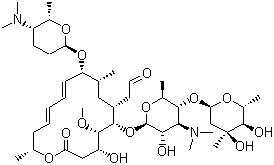



Spiramycin Supplier Casno 8025 81 8




The Binding Site Of Blasticidin S And Spiramycin On The 50 S Ribosomal Download Scientific Diagram




Effect Of Nitazoxanide And Spiramycin Metronidazole Combination In Acute Experimental Toxoplasmosis Sciencedirect



Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Jmedchem 6b Rand 3dkrshtg
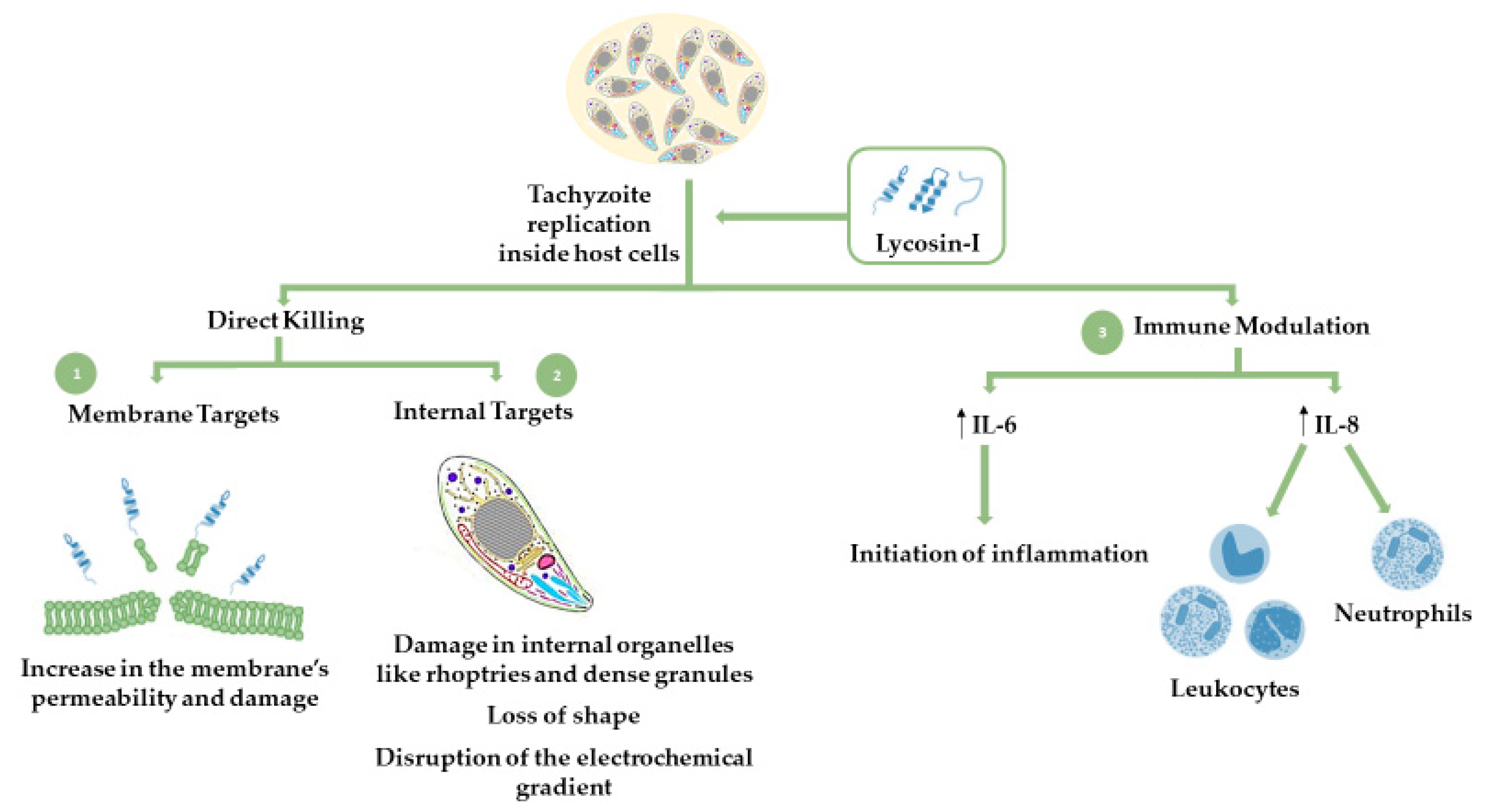



Molecules Free Full Text Antimalarial Agents As Therapeutic Tools Against Toxoplasmosis A Short Bridge Between Two Distant Illnesses Html




Antibiotics
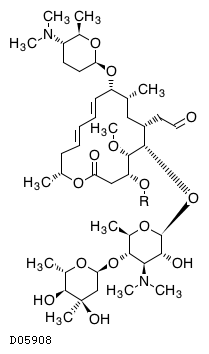



Kegg Drug Spiramycin
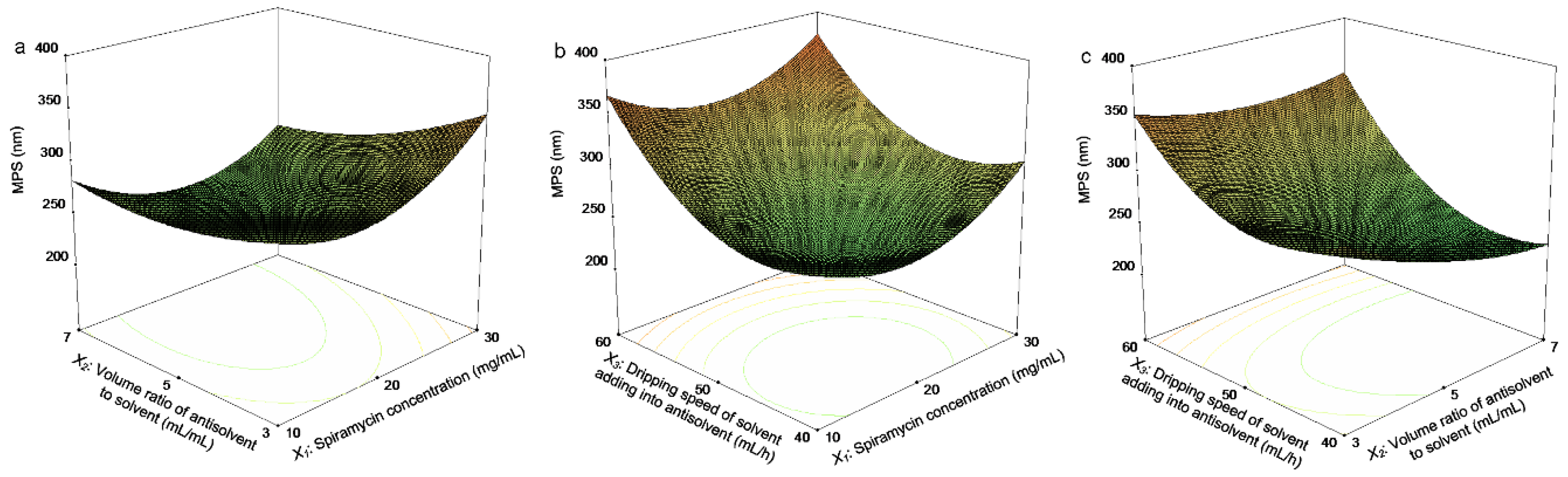



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Spiramycin And Azithromycin Safe For Administration To Children Exert Antiviral Activity Against Enterovirus 1 In Vitro And In Vivo Sciencedirect
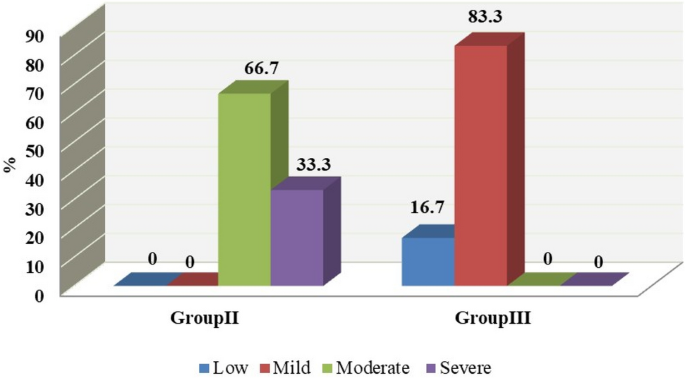



Effect Of Spiramycin Versus Aminoguanidine And Their Combined Use In Experimental Toxoplasmosis Springerlink




Spiramycin New Drug Approvals



Spiramycin Drug Monograph Druginfosys Com
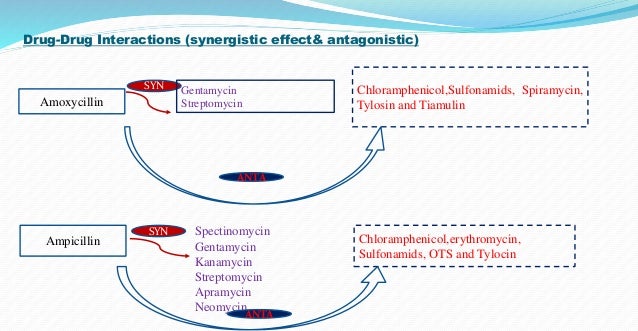



Antibiotics Classification Synergism And Antagonism




Target Identification And Intervention Strategies Against Amebiasis Sciencedirect
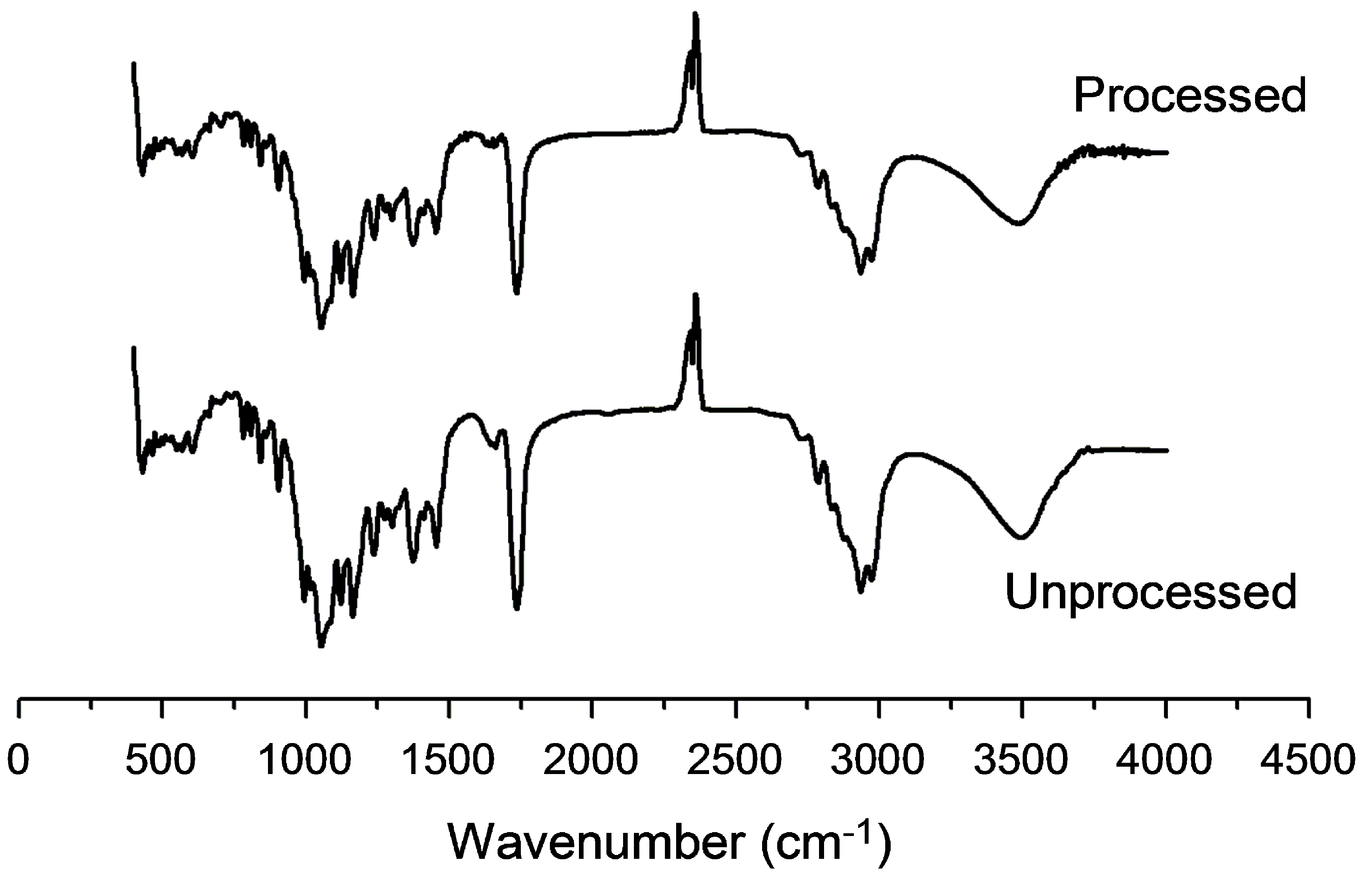



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Adsorption Of Metronidazole And Spiramycin By An Algerian Palygorskite Effect Of Modification With Tin Sciencedirect



Spiramycin I 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical



Spiramycin スピラマイシン New Drug Approvals




14 And 15 Membered Lactone Macrolides And Their Analogues And Hybrids Structure Molecular Mechanism Of Action And Biological Activity Sciencedirect




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




Spiramycin Semantic Scholar



Prof Khaled H Abu Elteen Ppt Download
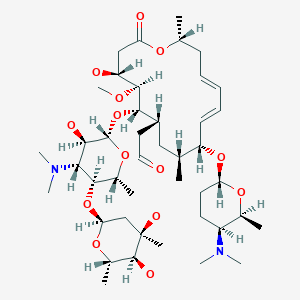



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
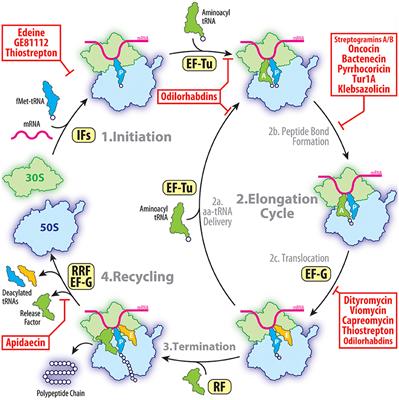



Frontiers The Mechanisms Of Action Of Ribosome Targeting Peptide Antibiotics Molecular Biosciences




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Pdf Study Of The Metabolism Of Spiramycin In Pig Liver




Two Dimensional Analysis Of Clindamycin Spiramycin Interactions Download Scientific Diagram




The Structures Of Four Macrolide Antibiotics Bound To The Large Ribosomal Subunit Molecular Cell
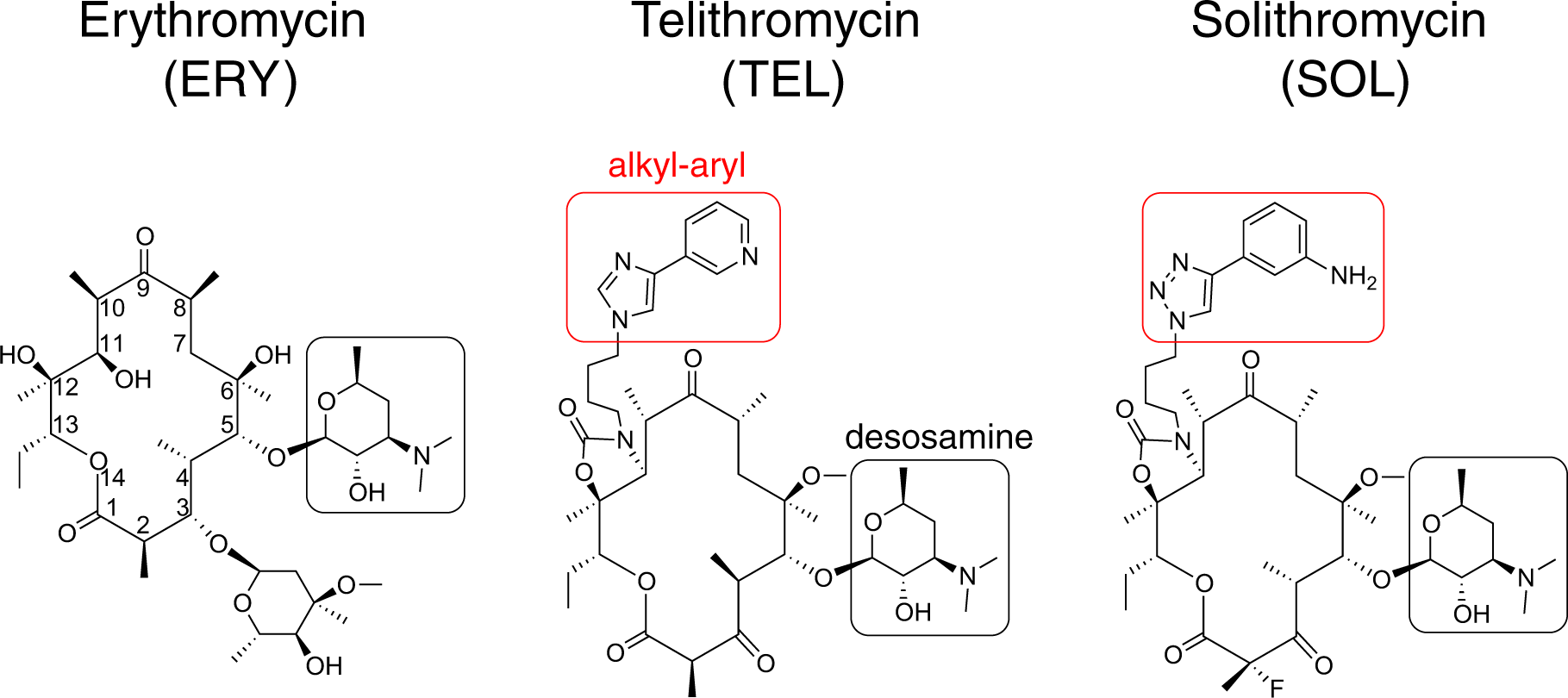



Context Specific Action Of Macrolide Antibiotics On The Eukaryotic Ribosome Nature Communications



Q Tbn And9gcth3d8x1nireuodgfhyz04qsitlwdy5u24hqn3wfh7gfdgiknay Usqp Cau
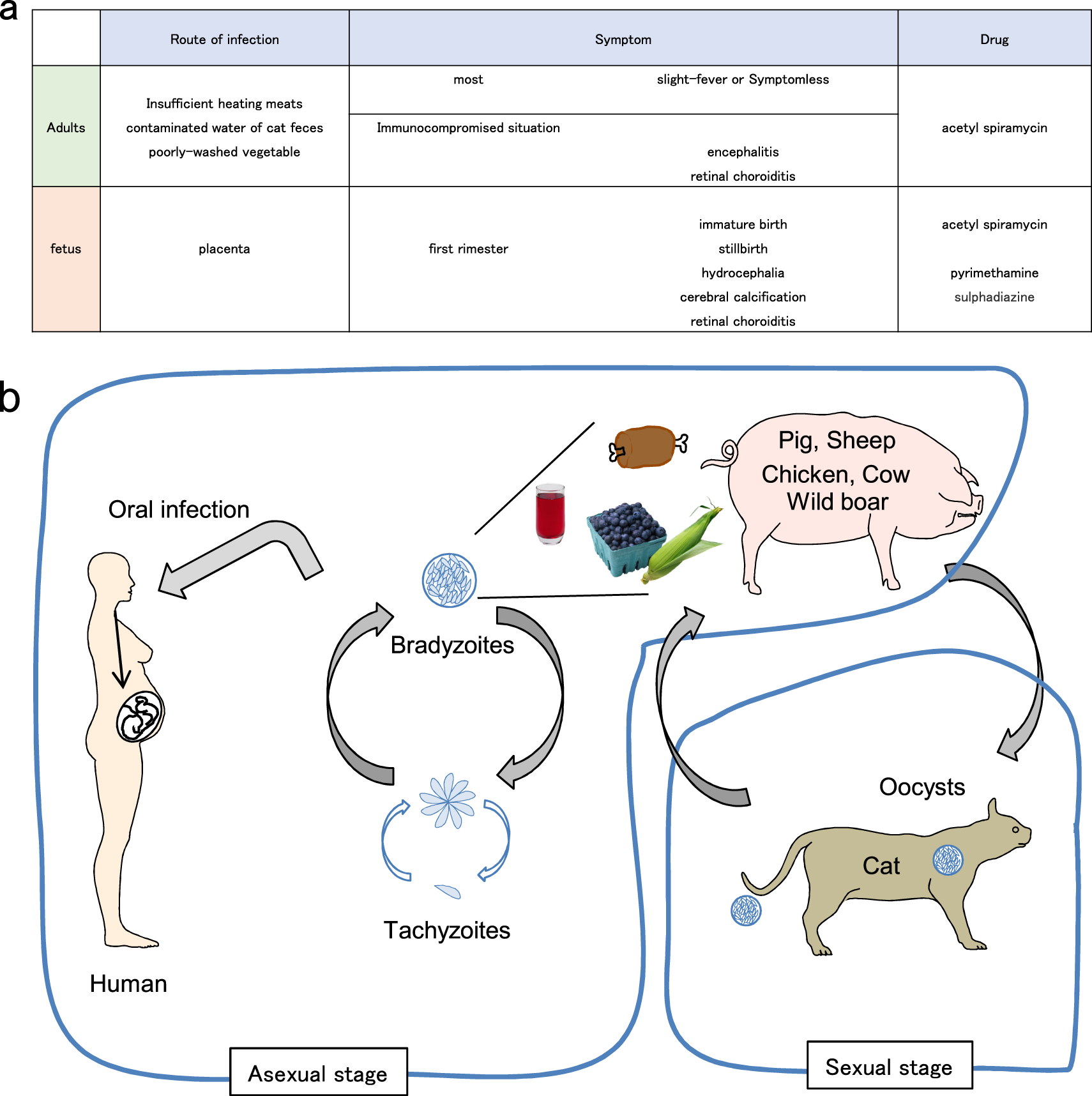



Innate Adaptive And Cell Autonomous Immunity Against Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Experimental Molecular Medicine



Http Citeseerx Ist Psu Edu Viewdoc Download Doi 10 1 1 321 7353 Rep Rep1 Type Pdf




Spiramycin Tablets Manufacturer Supplier Exporter



Www Toku E Com Converthtmltopdf Axd Product 481
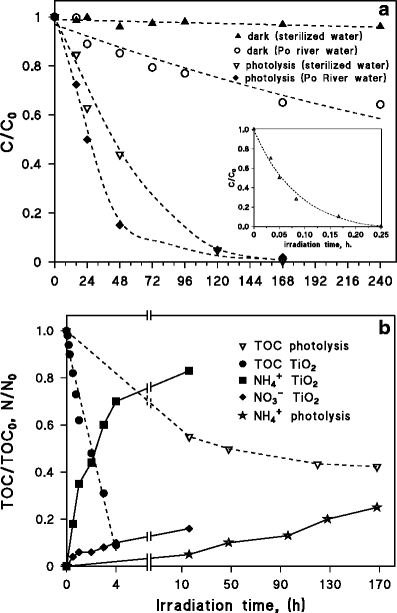



Fate Of Antibacterial Spiramycin In River Waters Springerlink




Spiramycin Wikipedia




Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Nucleic Acid Synthesis And Metabolism Ppt Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿